Chelidonichthys spinosus is a secondary economic fish species in China, which is increasingly being developed, utilized, and valued. However, it is considered one of the most depleted marine species in China due to overfishing.
Recently, the research team led by Prof. ZHANG Hui from the Institute of Oceanology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (IOCAS) has published a high-quality chromosome-level reference genome of Chelidonichthys spinosus in the Yangtze River Estuary.
The study was published in Scientific Data (a journal under the Nature publication group, Q1, 5-IF = 10.8) on July 12.
Chelidonichthys spinosus, commonly known as the spiny red gurnard in the order Scorpaeniformes, is mainly distributed in the Yellow Sea, East China Sea, and South China Sea, and has also been reported in the coastal waters of Japan, North, and South Korea. This species is a typical migratory fish that undertakes offshore overwintering migrations in late autumn and early winter, and returns to nearshore areas for spawning in the spring.
Due to its unique morphological characteristics, it has attracted significant attention. It has a snow-white belly, reddish-brown body, and underneath its gills, it possesses a pair of colorful, shimmering green fluorescent "butterfly wings". Below these "wings", there are three pairs of appendages resembling ballet dancers' "feet". In reality, these are six separate pectoral fins that are highly flexible and contain "taste buds" that aid in foraging. These distinct morphological features are closely associated with its ecological habits.
In an effort to investigate the evolutionary mechanisms behind the unique morphological features and ecological adaptations of C. spinosus, researchers performed deep sequencing of its genome using Illumina short-read, PacBio long-read, and Hi-C techniques, resulting in a high-quality chromosome-level reference genome.
The results revealed that the genome size of C. spinosus is approximately 624.7Mb, with a contig N50 length of about 13.77Mb and a scaffold N50 length of about 28.11Mb. A substantial 99.29% of the initially assembled sequences were successfully anchored to 24 chromosomes, and the genome contained 35.96% repeat sequences and 8,235 non-coding RNAs. A total of 25,358 protein-coding genes were predicted, of which 24,072 genes (94.93%) were functionally annotated. Co-linearity analysis showed a significant co-linearity between C. spinosus and Cyclopterus lumpus, suggesting a potentially close phylogenetic relationship between the two species.
"The assembled genome sequences can provide valuable information for elucidating the genetic adaptation and potential molecular basis of C. spinosus, which can be used to establish more effective management and conservation strategies for this species," said WANG Yibang, first author of the study.
"Additionally, these genomic data can also be used for future comparative genomics and phylogenetic studies, which may shed light on the genomic evolution and phylogeny of Scorpaeniformes and other teleost fish and vertebrates," added Prof. ZHANG.
The study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China and the Youth Innovation Promotion Association CAS, etc.
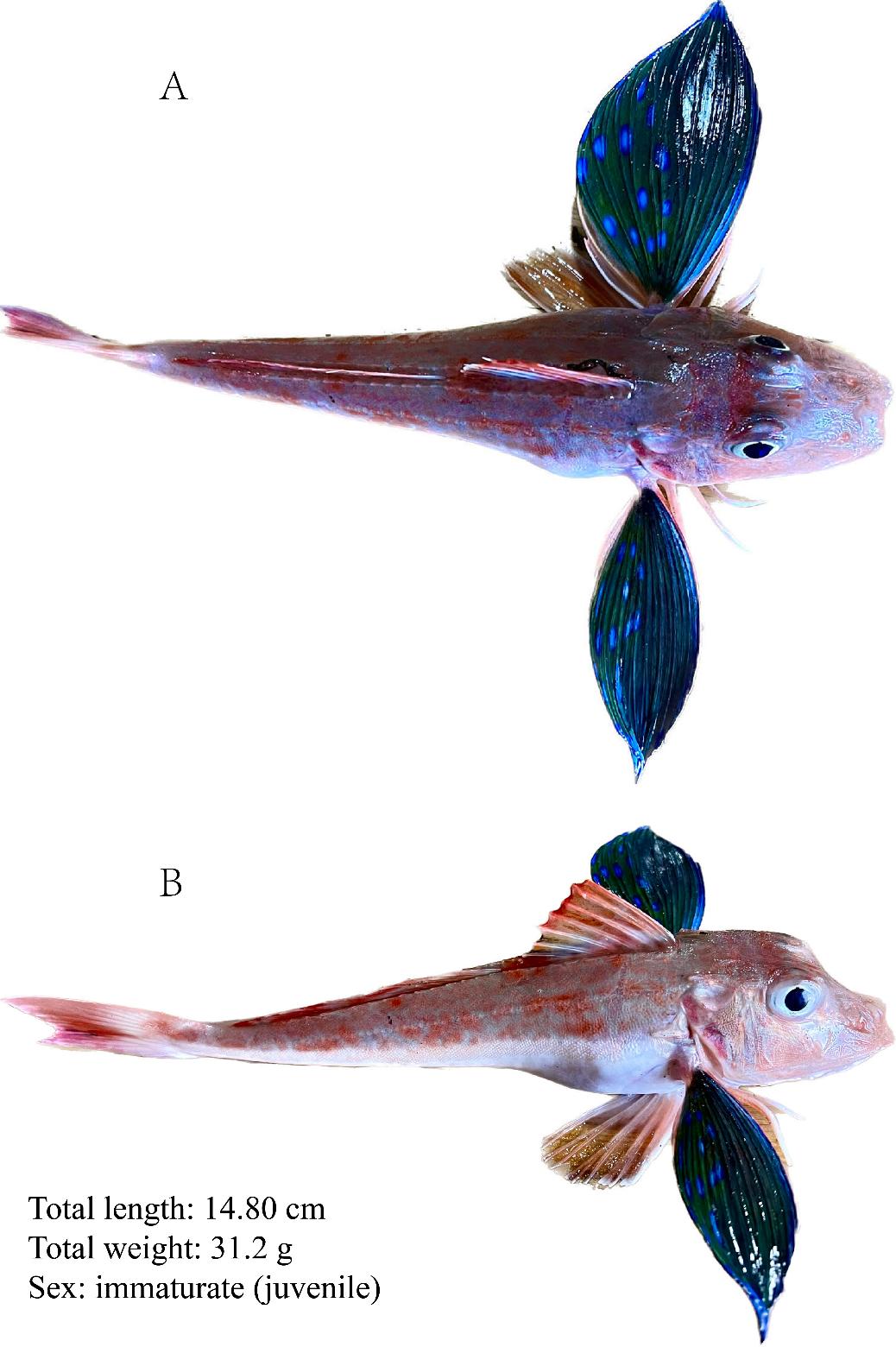

Fig. 1 Photography of Chelidonichthys spinosus specimen.
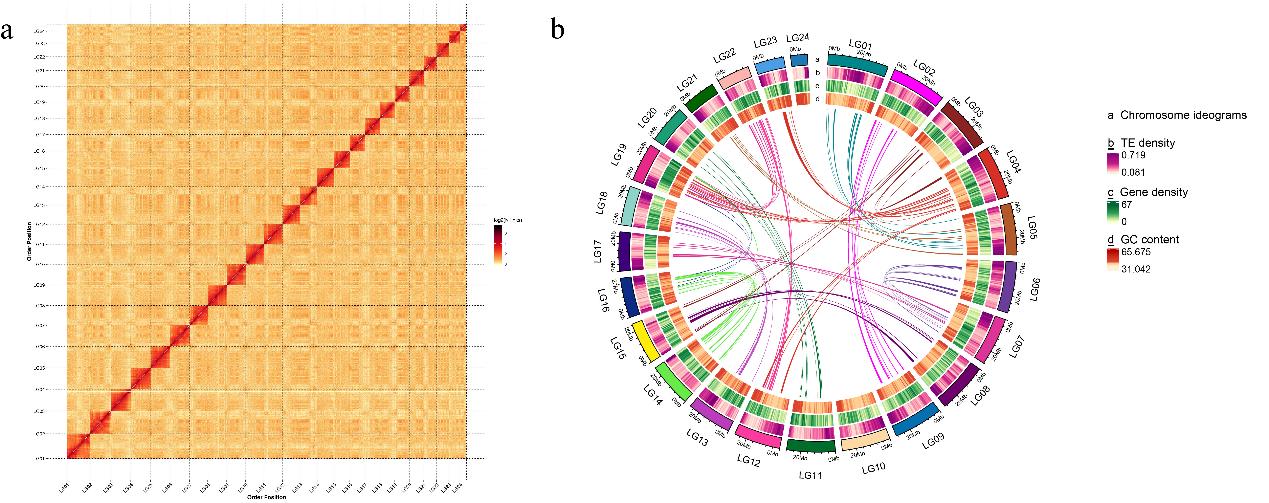
Fig. 2 Characteristics of the C. spinosus genome. (a) Hi-C intra-chromosomal contact map of the C. spinosus genome assembly. (b) Circos plot of the C. spinosus genome assembly.
Wang, Y., Zhang, H., Xian, W. Iwasaki W. (2023). Chromosome genome assembly and annotation of the spiny red gurnard (Chelidonichthys spinosus). Scientific Data, 10, 443.
(Text by ZHANG Hui)
Media Contact:
ZHANG Yiyi
Institute of Oceanology
E-mail: zhangyiyi@qdio.ac.cn
(Editor: ZHANG Yiyi)

