Recently, research team led by Weidong Sun from Center of Deep Sea Research, Institute of Oceanography, Chinese Academy of Sciences(IOCAS), conducted collaborative research with Prof. Dmitri A. Ionov from University of Montpelier, France, and Prof. Zhaofeng Zhang from Chengdu University of Technology. The latest research results on calcium isotopes of mantle peridotite containing carbonate inclusions were published in the Nature Index journal Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, which is helpful to understand the calcium isotope fractionation behavior of carbonate and silicate metasomatism in the mantle.
Mantle metasomatism is one of the most important geological processes that induce the heterogeneity of mantle materials. In addition to carbonate, there are also silicate melt and other media that cause mantle metasomatism. Therefore, a comprehensive understanding of the fractionation behavior and scale of calcium (Ca) isotopes in the mantle metasomatism caused by different metasomatic media is the basic prerequisite for the application of Ca isotopes to trace mantle metasomatism. Weidong Sun’s research team and collaborators worked on lherzolite and harzburgite xenoliths from Spitsbergen that were metasomatized, first, by silicate, then by carbonate-rich melts that formed carbonate-bearing pockets replacing earlier minerals (Fig. 1), which could deeply explore the behavior of Ca isotopes during silicate and carbonate metasomatism.
Seven crushed samples were treated with acetic acid that dissolved carbonates formed in the latest event, but not silicates. The results (Fig. 2) show that leachates (acid-removed carbonates making up 0.6–1.4% of total sample mass) contain much more Sr than the residues after leaching (277–2923 vs. 16–60 ppm), have a greater overall 87Sr/86Sr range (0.7049–0.7141 vs. 0.7036–0.7055) and higher δ44/40Ca in each sample than the residues. The leachates have lower δ44/40Ca range (0.17–0.68‰) than the residues (0.78–1.00‰), as well as lower δ44/40Ca than the residues in all samples but one. By and large, the carbonates are out of Ca-Sr isotope equilibrium with the host peridotites implying that the older silicate and younger carbonatite metasomatism were produced by different parental melts, thus supporting the existence of distinctive carbonate-rich metasomatic media in the lithospheric mantle, possibly including recycled materials.
The δ44/40Ca in the leachates (i.e. carbonates, 0.17–0.68‰) are well below bulk silicate Earth (BSE) estimates (0.94 ± 0.05‰) and δ44/40Ca in non-metasomatized melt-depleted mantle. Yet, δ44/40Ca in the non-leached whole rock (WR) carbonate-bearing samples (0.75–0.95‰) fall within, or are only slightly lower than, the BSE range. The δ44/40Ca range in these WR samples (0.7030–0.7112) includes very high values for peridotites with large aggregates of dolomite and Mg-calcite. It appears that both carbonatite and silicate metasomatism may produce δ44/40Ca values lower than the BSE such that Ca-isotope data cannot robustly tell apart these two enrichment types, yet carbonatite metasomatism may yield the lowest δ44/40Ca. Carbonates, even at small mass fractions, are significant hosts of Sr in the WR Spitsbergen peridotites (8–51 wt.% of Sr mass) because of very high Sr concentrations, but add little to WR Ca balance (3–12 wt.%). As a result, high Sr content and 87Sr/86Sr ratios may be indices (though not definitive proofs) of carbonatite metasomatism in mantle rocks.
This study was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41773009 and 41873002) and the Programme National de Plane′tologie (PNP) of CNRS/INSU/CNES (grants to DAI in 2018-2019). The first author of this paper is associate researcher Hongli Zhu from Center of Deep Sea Research, IOCAS, and the corresponding author is Prof. Dmitri A. Ionov from University of Montpelier, France.
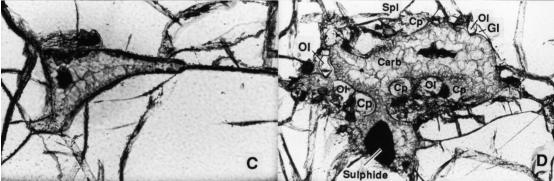
Fig. 1 Photomicrographs of carbonate-bearing Spitsbergen xenoliths.
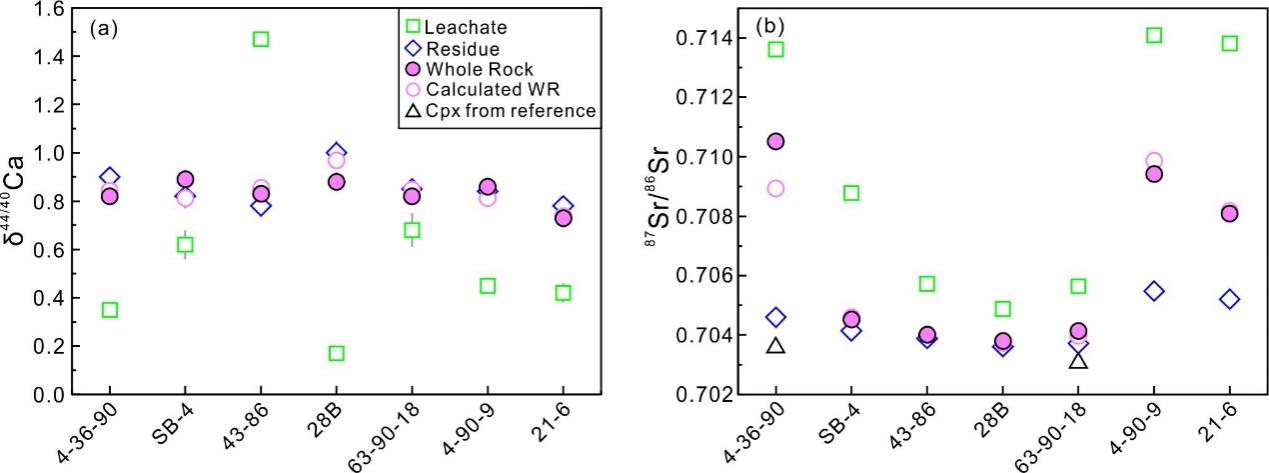
Fig. 2 Comparisons of δ44/40Ca and 87Sr/86Sr in leachates, residues and whole-rocks for carbonate-bearing Spitsbergen xenoliths.
Hongli Zhu, Dmitri A. Ionov*, Long Du, Zhaofeng Zhang, Weidong Sun. Ca-Sr isotope and chemical evidence for distinct sources of carbonatite and silicate mantle metasomatism. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2021(312): 158-179. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0016703721004701.
(Editor: ZHANG Yiyi)

