Predicting the extent of September Arctic sea ice carries significant implications for climate change and Arctic shipping. However, seasonal-scale forecasts of September Arctic sea ice extent exhibit a "spring predictability barrier".
To tackle this issue, the research team led by Prof. LI Xiaofeng from the Institute of Oceanology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (IOCAS) has developed a new AI model, SICNetSeason, for predicting the Arctic on a seasonal scale.
The study was published in Geoscientific Model Development on May. 14.
Traditional numerical model-based sea ice prediction methods, such as the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF)'s SEAS5 and statistical model-based approaches, frequently encounter Arctic sea ice spring predictability barrier.
The SICNetseason model integrates the nonlinear global and local dependencies among sea ice series by Swin-Transformer blocks. It can model the long-term dependencies between the spring sea ice states and the September sea ice to achieve more accurate predictions than numerical and statistical models.
Experimental results show that when predicting September Arctic sea ice extent using April/May as the initial months, the SICNetseason model achieves 7–10% higher predictive skill (ACC) and over 14% improvement in sea ice boundary accuracy (BACC) compared to the globally leading ECMWF seasonal forecasting system SEAS5, significantly reducing the spring predictability barrier. Spring sea ice thickness is recognized as a critical factor, contributing more than 20% to alleviating this barrier.
This study provides an AI-driven solution to the Arctic sea ice spring predictability barrier, advancing the precision of seasonal-scale sea ice forecasts for September in the Arctic.
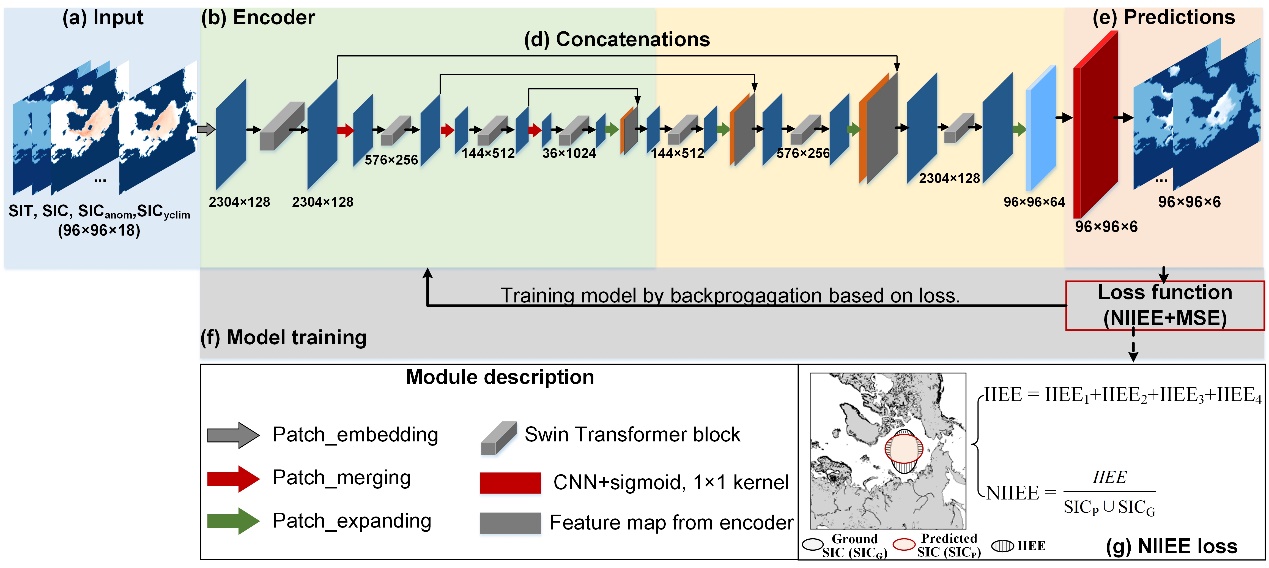
Framework of model SICNetseason. (Image by IOCAS)
(Text by REN Yibin)
Media Contact:
ZHANG Yiyi
Institute of Oceanology
E-mail: zhangyiyi@qdio.ac.cn
(Editor: ZHANG Yiyi)

