The increasingly serious global environmental pollution has brought serious problems to the cultural development of human society. Up to now, a large number of photocatalysts have been studied in terms of environmental pollution and bacterial infection. Some photocatalysts are considered as potential catalysts because of their superior separation, reusability, controllability, and environmental friendliness.
However, photocatalysts can't play a role under dark conditions. Thus, enzyme-like activity has been found to produce reactive oxygen species (ROS) without visible light, solving the weakness of photocatalysts. Development of an effective catalyst with photocatalytic and enzyme-like activities is of great significance for improving the utilization efficiency.
Recently, the research team led by Prof. Wang Yi of Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences (IOCAS), found new insight into photocatalytic and enzyme-like activities. The study was published in Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects. The derived technical achievements have been declared and patented Chinese National Invention Patent.
Researchers found that AgBr/Ag2MoO4 possesses excellent photocatalytic activity and high enzymatic activity.
The oxidase-like and peroxidase-like activities of AgBr/Ag2MoO4 were examined by oxidizing 3,3',5,5'-tetramethylbenzidine (TMB) to oxidized TMB (oxTMB). 1:1AgBr/Ag2MoO4 exhibited the highest peroxidase-like and oxidase-like activities of the prepared samples, while the pure AgBr and Ag2MoO4 showed low oxidase-like and peroxidase-like activities.
The photocatalytic property of AgBr/Ag2MoO4 was measured through the degradation experiment of Rhodamine B (RhB) and tetracycline hydrochloride (TC) under visible light. 1:1AgBr/Ag2MoO4 composite displayed the highest photocatalytic activity of RhB that among the materials in this study, and its degradation rate reached nearly 100% in 60 min. For TC, the photo-degradation rate achieved nearly 73% within 120 min, which was also the highest result. It was evidenced that AgBr/Ag2MoO4 could degrade more RhB in a short time than the similar content of other photocatalysts.
Then, the sterilization rate under the synergistic effect of enzyme-like and photocatalytic activities reached 100% in a short incubation time, which emerged the limitation of single light and H2O2, confirming the synergistic effect of photocatalysis and enzyme-like catalysis.
Thus, this study demonstrated that the AgBr/Ag2MoO4 possessed dual catalytic performance for the enhanced bactericidal application, which had high antifouling effect. Researchers believe that AgBr/Ag2MoO4 composite would be potentially used in environmental pollution, bacterial infection, and other catalytic fields.
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China and High-end Users Program of "Kexue".
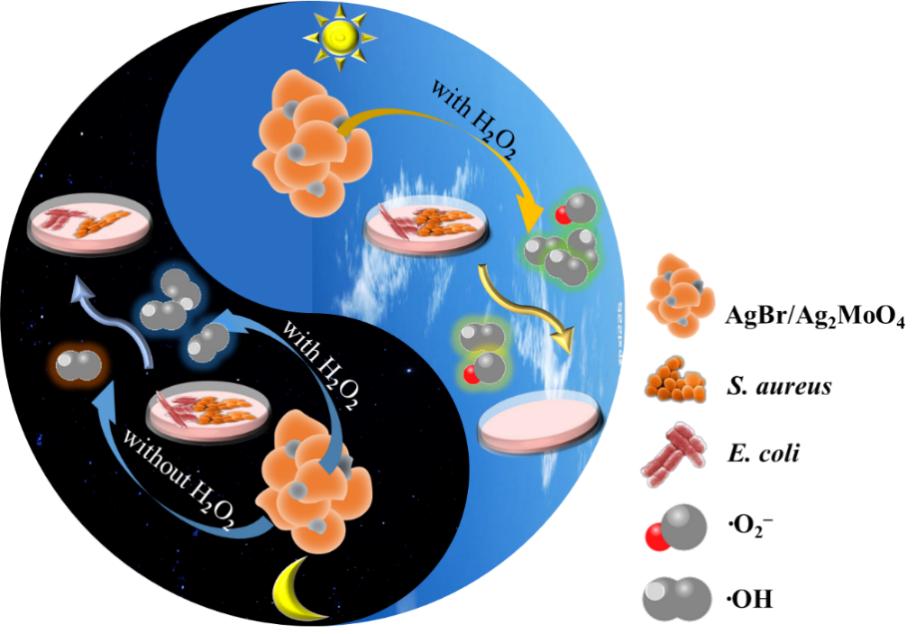
The illustration image of the synergistic effect of photocatalysis and enzyme-like catalysis about AgBr/Ag2MoO4
Yumeng Lian, Yi Wang*, Dun Zhang, Likun Xu. (2022). Visible Light-driven Photocatalytic and Enzyme-like Properties of Novel AgBr/Ag2MoO4 for Degradation of Pollutants and Improved Antibacterial Application. Colloids Surf., A, 128348.
WANG Yi
Institute of Oceanology
E-mail: wangyi@qdio.ac.cn
(Editor: ZHANG Yiyi)
|
|

Address: 7 Nanhai Road, Qingdao, Shandong 266071, China
Tel: 86-532-82898902 Fax: 86-532-82898612 E-mail: iocas@qdio.ac.cn


