The blue mussel Mytilus edulis, which is a common species of the family Mytilidae, is widely distributed and cultured in coastal waters, where it plays an important role in the food web and carbon cycle and is a valuable fishery and mariculture commodity. However, as coastal eutrophication rapidly worsens in many regions, both the intensity and duration of hypoxic events increase tremendously, posing a great threat to blue mussels.
To date, most studies of blue mussels under hypoxic stress have been confined to a timescale of hours, and previous research has mainly looked at acute physiological or biochemical responses, leaving the impact on mussel survival as well as on their population densities unknown.
Recently, the research team led by Prof. SUN Song from the Institute of Oceanology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has determined the critical threshold of dissolved oxygen (DO) concentration for the survival of blue mussel, in an experiment covering the range DO 0.5-2.0 mg L-1 during 16 days of exposure. The impact of DO fluctuations and poor water quality were further assessed. The responses of metabolic rate and several key enzymes were analyzed to identify possible physiological stresses.
The study was published in Marine Environmental Research on Mar. 15.
According to the results, the critical threshold of DO for experimental mussels exposed to 16 days of hypoxia was 0.7-0.8 mg L-1 ,below which survival dropped drastically from nearly 80% to <38%. When hypoxia was combined with DO fluctuations or with poor water quality, the threshold could further rise as the mussels under combined threats suffered higher mortality than those under the single stress of hypoxia.
In the following physiological and biochemical analysis, it is found that the blue mussel is an oxygen-conformer that depressed its respiration rate as well as the individual's total energy requirement when the DO concentration falls below 5-6 mg L-1 .Among all the enzymes analyzed, acid phosphatase and alkaline phosphatase were the most sensitive ones, suggesting that a compromised immune response is another important factor challenging the survival of blue mussel in addition to energy deficiency.
"In general, the blue mussel has a strong tolerance against hypoxia, and a moderate hypoxia event is less likely to cause mass mortality. However, it is worth noting that the survival rate was significantly lower when the DO was at a moderate level of 1.0 mg L-1 but the experimental conditions included a doubled population density, no water change, no water purifier, and no Ultraviolet lamp illumination," said LI Qiao, first author of the study. "Thus, we strongly recommend that both the DO concentration and the spread of pathogens should be closely monitored in blue mussel mariculture, and that the stocking density should be relatively low under a risk of hypoxic conditions."
"The findings will help to predict the fate of blue mussels under increased hypoxic events and provide scientific advice for mariculture management," said Prof. SUN.
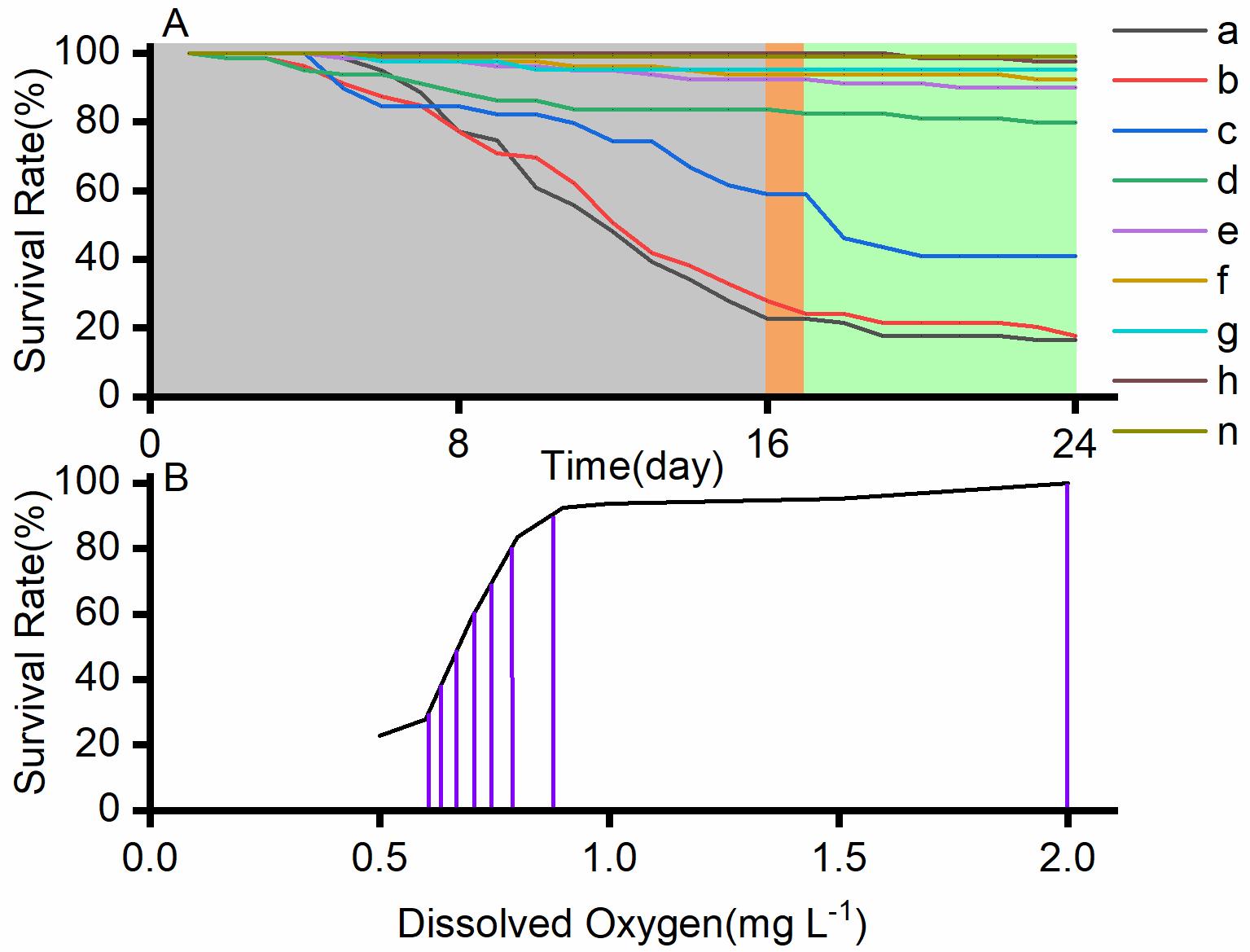
Changes in the survival rate of blue mussels under hypoxia at different dissolved oxygen concentrations
LI Qiao
Institute of Oceanology
E-mail: liqiao@qdio.ac.cn
(Editor: ZHANG Yiyi)
|
|

Address: 7 Nanhai Road, Qingdao, Shandong 266071, China
Tel: 86-532-82898902 Fax: 86-532-82898612 E-mail: iocas@qdio.ac.cn


