As the origin of the western boundary currents and the boundary between tropical and subtropical gyres in the North Pacific, the North Equatorial Current (NEC) plays a significant role in the water mass balance and heat budget of the North Pacific.
Recently, the research team led by Prof. HU Dunxin from the Institute of Oceanology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (IOCAS) provided new insight into the study of intraseasonal variability (ISV) of the North Equatorial Current and North Equatorial Undercurrent. Two flavors of ISV signals with different vertical structures were detected by mooring acoustic Doppler current profile (ADCP) measurements at 13°N, 130°E, and their dynamics were revealed.
The study was published in Frontiers in Marine Science on Mar. 28.
Prominent intraseasonal fluctuations in both the surface and subsurface layer of the NEC and its associated undercurrents-North Equatorial Undercurrent (NEUC) have been reported, and eddy activities are playing important roles in the modulation of the ISV in the NEC region. The vertical modes of the ISV across the 130°E section exhibit different structures at different latitudes. The ISV at lower latitudes (south of 13°N) appears to be dominated by subthermocline-intensified signals, while the ISV at relatively higher latitudes (north of 13°N) is dominated by surface-intensified signals.
"Based on the continuous in-situ measurements of the mooring ADCP, we found significant surface-intensified ISV with a higher frequency and subsurface-intensified ISV with a lower frequency exist simultaneously in the upper 800m at 13°N, 130°E. This interesting pattern of velocity variances seems to be ignored by previous studies, and its dynamics remain unclear," said WANG Zhenxiao, first author of the study.
Researchers used data from satellite and an eddy-resolving ocean general circulation model for the Earth Simulator to investigate the properties and source of these two flavors of ISV signals. They found that the surface-intensified (subsurface-intensified) ISV signals are related to the surface (subsurface) eddies locally generated between 130°E and 135°E.
"Based on the energy analysis and stability analysis of the background flow in the NEC region, this research suggests that the surface-intensified ISV is mainly due to baroclinic instability of the surface current in the upper 400m, while the subsurface-intensified ISV is mostly induced by barotropic instability of the subsurface currents between 400-600m," said Prof. HU.
The research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the National Key Research and Development Program of China, and the Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
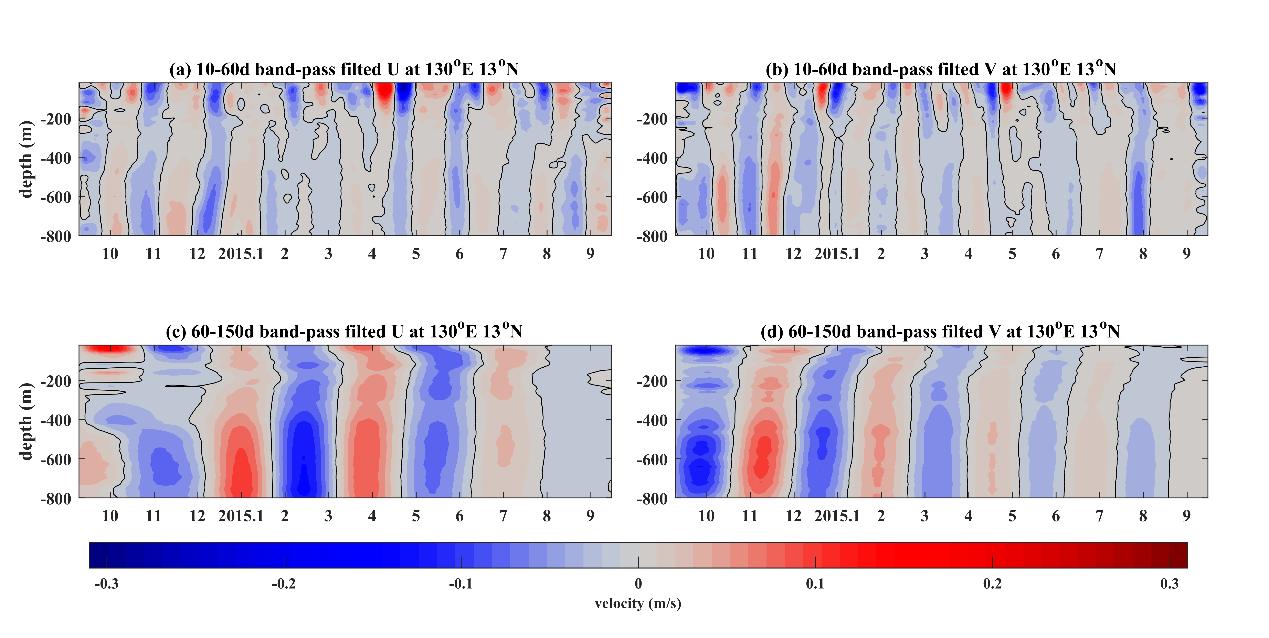
(130°E, 13°N) Two flavors of ISV signals with different periods and different vertical structures were detected by mooring ADCP measurements
Z. Wang, L. Zhang, Y. Hui, F. Wang, and D. Hu. (2022). Two Flavors of Intraseasonal Variability and Their Dynamics in the North Equatorial Current/Undercurrent Region, Front. Mar. Sci., vol. 9.
WANG Zhenxiao
Institute of Oceanology
E-mail: wangzhenxiao@qdio.ac.cn
(Editor: ZHANG Yiyi)
|
|

Address: 7 Nanhai Road, Qingdao, Shandong 266071, China
Tel: 86-532-82898902 Fax: 86-532-82898612 E-mail: iocas@qdio.ac.cn


